

Stocks vs Options: Which Is Better?
Options are a newer trading investment compared to stocks that have been known and used by most investors. To help you decide which is better for you, or if you'll lean toward combining the two, here are several factors you need to consider about the difference between stocks and options.
What Are Options?
A stock option (or simply an option) is a derivative security, meaning that its value is derived from an underlying security. It's a contract that gives investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a certain or fixed price, commonly known as the strike price, at a specific date or time (also referred to as the expiration date).
Options trading is an advanced investment strategy that helps investors increase their profit and limit risks. An options contract constitutes 100 shares of stock, and the contract owner has the choice to exercise the contract before it expires or let it expire. Buying an options contract doesn't mean you purchased a stock unless you exercise the contract.
If you exercise the contract, you buy or sell the shares in the contract at a strike price before it expires. The price of the underlying stock or asset has a vital role in your choice.
Types of Options
Options have two types, and they are as follows:
Call Options
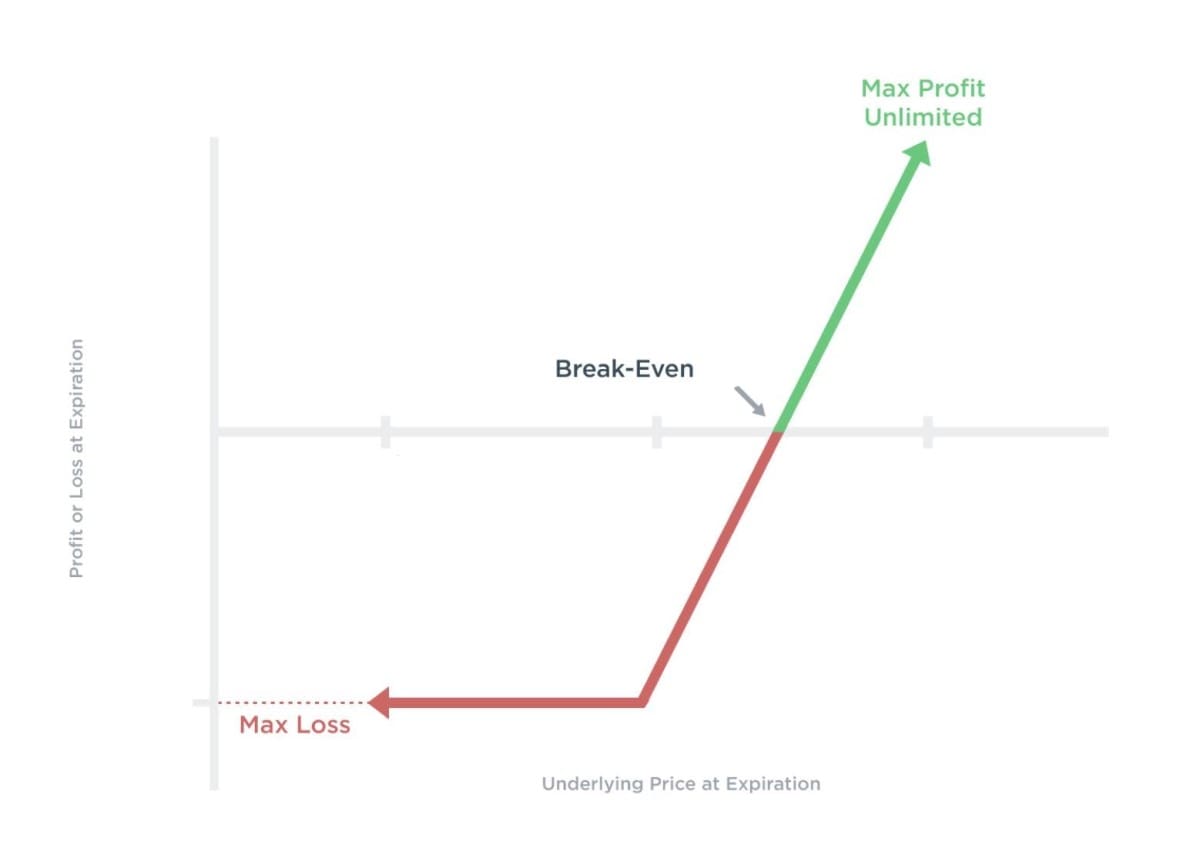
Call options allow the option holder or option buyer to purchase an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) until a specific date or expiration date. When the price of stocks increases, the value of the call option also increases. If you want to have a call option contract, it's because you expect the stock price to increase.
Here's a simple example of a call option:
Company A offers underlying security with a $100 strike price and an option premium of $10 or a total of $1,000 premium (multiplied by 100 shares since options contracts cover 100 shares) until May. If the company's stocks reach a price of $150 before May, your profit will be $40 or $4,000 in total.
| $150 (Underlying Security) – ($10 Option Premium + $100 Strike Price) = $40 Profit Per Share |
| $40 Profit x 100 shares = $4,000 Total Profit |
Put Options
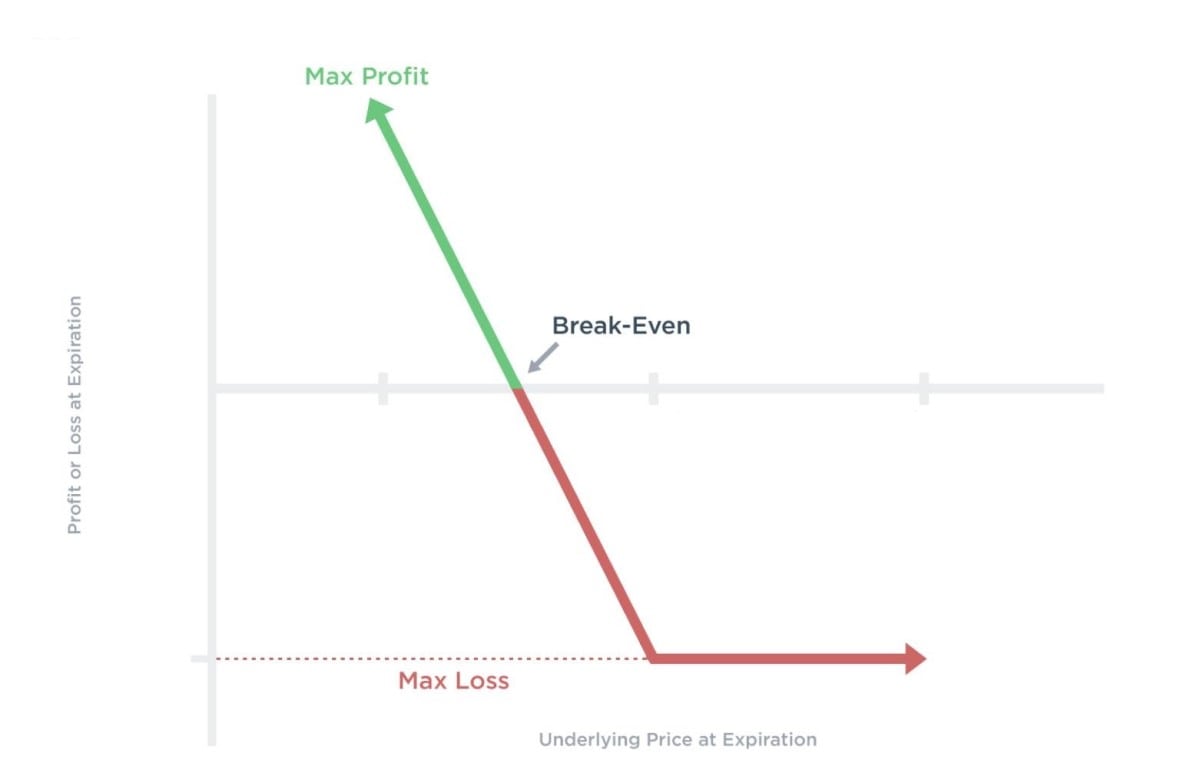
Put options are contracts that allow the owner to sell the underlying stock at a predetermined price (strike price) until a specific date or expiration date. When the price of stocks decreases, the value of the put option increases. If you buy a put option, you're expecting the stock price to fall.
Here's a simple example of a put option:
Company B trades a stock at $150 per share. You will buy a put option with a strike price of $100 and an expiration date of four months. The premium cost is $10 per share and $1,000 in total for 100 shares. Company B's stocks should drop to less than $90 (the breakeven point) to gain profit.
| $100 Strike Price - $10 Option Premium = $90 Breakeven Point |
The Pros and Cons of Options
Options, like other investments, have several advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Trading in Options
- Only requires small capital. If you buy an options contract, you'll only pay a fraction of the value of shares to gain exposure to a stock. A small investment will be enough to participate in market activity.
- A very good hedge.Options trading can be used with other stock holdings to produce additional income or hedge a position. For example, you can purchase a put option to protect you against downside risk.
- Lucrative if done right. Depending on your strategy, if you do options trading right, it'll be a great addition to your financial portfolio.
Disadvantages of Trading in Options
- Expiration.Options have expiration dates meaning you have a limited time to plan what to do with your investment.
- Value decreases with time. As the options get closer to the expiration date, the value decreases. This is the reason why some options expire with zero value.
- Short-term. You'll still need to pay taxes at your regular income tax rate instead of the long-term capital gains tax rate on any gains earned on options.
What Are Stocks?
Stocks are also known as equities and are the most common tool used by investors. It's a type of security that represents percentage ownership or you own a share of ownership in a company.
For example, you buy $10 per share of company stock, and the price increases to $15 per share. This would mean a 50% profit if you sell your shares.
Types of Stock
Here are the different types of stocks explained:
Preferred Stocks
Owners of preferred stocks usually don't have voting rights. But they have superior claims than common stock owners on the company's assets. They receive dividends before common stockholders and are the priority if assets are liquidated, or the company goes bankrupt.
Common Stocks
The common stock position offers ownership in the company and the right to vote and receive benefits such as dividends, stock bonuses and others. However, like what was previously mentioned, they're not prioritised over those with preferred stocks.
The Pros and Cons of Stocks
Like options, buying and selling stocks has its set of benefits and risks as market prices are volatile.
Advantages of Investing in Stocks
- Low capital or cost of entry. Some online brokers allow investors to buy fractional shares of stock for as low as $5 and even $1.
- Right to dividends. If you're a shareholder of stocks, you'll receive dividends. Dividends can potentially provide long-term and short-term gains.
- No limit to the holding period. You can have your shares as long as the business is operating as a publicly-traded company.
Disadvantages of Investing in Stocks
- Stock prices fluctuate. The prices of stocks can fluctuate remarkably, which means that you can't sell a stock for any given price.
- Prices of stocks depend on the company's performance. Therefore, you'll need to find the right companies by doing in-depth research to grow, earn and succeed alongside them.
- Any gains are taxable. However, if you lose money, you can get a tax write-off.
Key Differences Between Stocks and Options
The major difference between stocks and options trading is that options are contracts with other investors. You'll bet on your market assumption or the direction where stocks are headed. In contrast, stocks represent shares of ownership in various individual companies.
While it's compelling to gain profits within the stocks and options trading, it'll be advantageous to learn more about Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) and low-cost index funds. They can also serve as a good entry point for traders and investors who are just beginning to diversify their portfolios.
Stock vs Options Comparison Table
To guide you with your investment strategy, below is a comparison table between options and stocks.
|
Basis of Comparison |
Stocks |
Options |
|
Meaning |
They come with the right to ownership of a share of a company. |
They are contracts that give traders or investors the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell shares of underlying stocks for a fixed price until the expiration date. |
|
Type of investment |
Equity |
Derivative |
|
Benefits |
Possible dividend payments, stock bonuses, voting rights and less hands-on attention. |
Potential returns and a possible hedge against market volatility. |
|
Used by |
Individuals or beginner investors, long-term investors, hands-off investors, mutual funds and pension plan managers. |
Active traders, employees, advanced investors and fund managers |
|
Time horizon |
Usually long-term, up to 6 to 10 years |
Usually short-term, from weeks to months |
|
Risks or potential drawbacks |
Lower risk when used appropriately |
Very risky because all the capital or money used can be gone quickly |
Which Is Better for You?

Choosing between options or stocks about what's best for you is entirely a personal decision. Having said this, you need to take into consideration the personal factors affecting your investing style. If you're new to investing, you can stick to stocks as they are more straightforward and less risky. However, if you prefer an active and quick investment approach, options can be a good choice.
If you can take risks and want to combine the two, that's also a viable strategy. Many stock traders put options as their hedging mechanism, so it's not uncommon.
Additionally, you must know what type of investor you are. This will help you choose what kind of investment is right for you. For example, when you encounter the term bullish, it pertains to an investor who believes that bonds, a few stocks or the stock market as a whole will rise in price in the future. On the other hand, a bearish investor is someone who thinks that the stock market's future performance will go down.
Why Should You Choose OptionsOver Stocks?
If you want to get a more tactical approach to investing and limit your risk, so you only use a certain amount of money, options are the way to go. Since the investment time is shorter, it's more attractive to traders who buy and sell regularly. However, please keep in mind that even with limited risk, you can still incur losses.
When Should You Invest in Stocks Over Options?
If you're a beginner investor, you should get comfortable with stock trading before buying options. Moreover, if you plan to invest and let your capital work for a long period of time, stocks can be good for you. You can count on long-term movements, which isn't the case with options; those focus more on short investment durations.
Conclusion
Options and stocks have their pros and cons, and they both offer different returns. Choosing what's right for you will depend on your preference and financial strategy. What's important is you know what they are and how they work before you get involved.
Now that you know the difference between stocks and options, you can use this knowledge and practise in a Libertex demo account to hone your skills and trading.
FAQ
Why Are Options Riskier Than Stocks?
Options can be riskier than stocks because they are short-term investments. They are also derivative securities that are more volatile. If the stock market decreases or moves unfavourably before their expiration date, you can lose your original capital or even more than what you invested in them.
Can I Lose More Money in Stocks Than Options?
Losing all your option premium or capital on expired options and unlimited risk and loss in naked call options is more likely than a stock's value dropping to zero. Remember that options have expiration dates that only take weeks to months. If the market price moves unfavourably, they become worthless.
Why Do Some Stocks Not Have Options?
Stocks that trade in over-the-counter markets or with limited public interest are less likely to support options trading because options are only attractive if those options can be bought or sold easily.
Can You Invest in Stocks and Options at the Same Time?
You can invest in both stocks and options at the same time if you want to. After understanding what stocks and options are and how they work, you can either add to your portfolio or invest in them simultaneously.
Should You Day Trade Options or Stocks?
Stocks are one of the most common in day trading markets, along with foreign exchange (forex) and futures. So, if you want to day trade, it's better to trade what's common in the market. After all, there is a reason why many investors choose them. But before putting your money at risk, try practising your strategy on a trading simulator or demo account first.
Do Options Make More Money Than Stocks?
Although options can be riskier than stocks if traded correctly, they can be more profitable than traditional stock investing. That's not the case for everybody, but it's a real possibility.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to be and does not constitute investment advice or any other form of advice or recommendation of any sort offered or endorsed by Libertex. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Why trade with Libertex?
- Get access to a free demo account free of charge.
- Enjoy technical support from an operator 5 days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. (Central European Standard Time).
- Use a multiplier of up to 1:30 (for retail clients).
- Operate on a platform for any device: Libertex and MetaTrader.