
Spread Trading For Beginners: What is a Spread In Forex CFD trading?
One of the key competitive assets of most brokers in the forex market is the spread size for currency pairs.
A spread determines the future costs a trader will have to face, which makes it a valuable term to learn.
To comprehend what a spread is, imagine any trading operation, such as buying clothes for resale. The difference between the price originally paid and the money received is called profit or income. A spread works similarly, and brokers receive income on the spread.
What is a Spread, and How Does it Work?
The spread is the difference between the Bid and the Ask prices of each currency from a currency pair. This is a direct initial loss for the trader, which should be covered in further trading.
Let's give an example using the popular EUR/USD pair with a hypothetical quote of 1.1152/1.1156. From the difference in the currency value, it can be seen that the spread for one lot, in this case, is 4 pips. To compensate for this loss, you want the currency pair quotes to change in your favour by at least 4 pips. Once this happens, you'll start receiving a profit.
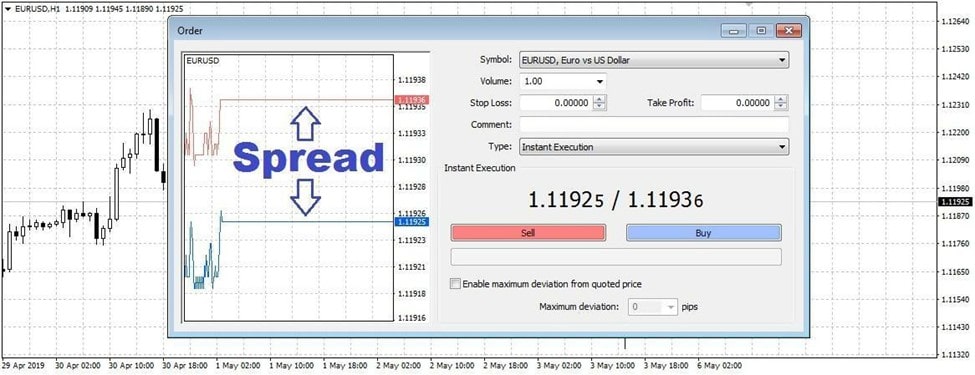
After making a transaction, you get a loss which equates to the spread. It happens because you acquired a currency pair at a price slightly higher than the market price (the gap between your price and the market price is already a broker's fee). Therefore, it becomes an inevitable compulsory commission.
How to Calculate Spread
Spread = Ask (the price a buyer is willing to pay) - Bid (the price at which a market maker is willing to buy). Once again, set in pips for convenient calculation.
For example, if the price of the GBP/USD currency pair has a Bid price of 1.2920 and an Ask price of 1.2923, then the Spread = 1.2923-1.2920 = 0.003 USD or 3 pips.
Why Calculate the Cost of the Spread?
Calculating the spread cost during the trading process is necessary for building proper trading strategies, primarily automated ones, and for technical analysis of the current situation. The spread cost in the amount of profit becomes more significant when the position stays open for less time and when the frequency of transactions in the trading system gets higher.
Spread cost = Spread size*Lot size*Number of lots
Let's estimate the spread cost from the example above. The lot size is $100,000.
0.0003*$100,000*5 = $150.
What Affects a Spread in Forex Trading
Liquidity
The greater the number of market participants engaged in trading in a currency pair, the closer the prices at the time of the transaction. The spread size usually does not exceed 3-5 pips in the most popular pairs. When trading rarer currencies, for example, the Canadian dollar or the Swedish krona, this figure can reach 50 pips and higher.
Most brokers offer a minimum amount of spread on popular currency pairs, mainly profiting from a larger number of transactions.
Current market situation
Important economic news, statistical information and the market's panic-crash generate an instant and significant change. Generally, the situation depends on economic and political factors in different countries and the world community. Any news can significantly affect the rates of leading currencies. For example, when, on the one hand, a large number of buying orders withdraw from the market and, on the other hand, selling orders lag, it leads to an increase in the spread.
Broker's policy
Most brokers limit and guarantee the maximum spread size for given currency pairs within their commission schedule. But remember that this is how they make a profit, and there cannot be brokers with zero spread accounts without them charging a commission.
Types of a Spread
There are two types of spreads: fixed and variable. Below we explain their differences, advantages and disadvantages.
Fixed Spread
A fixed spread is a constant value regardless of currency fluctuations. This type is set on the most liquid currency pairs where average spread fluctuations are insignificant. In some cases, a broker can increase a spread manually depending on the investment, economic and financial forecasts.
Most often, a fixed spread is set for EUR/USD, EUR/GBP, USD/JPY and GBP/USD currency pairs.
Advantages
- Fixed spreads allow traders to rely on a strategy without worrying about unexpected variables.
- Trading with fixed spreads works as a cheaper option because it calls for smaller regulatory capital. It's best for beginner traders who can't afford to invest a lot of money when just starting out.
- It provides the trader with the predictability of initial costs in each transaction.
Disadvantages
- It can't be used during scalping.
- You are likely to get new prices because your broker won't be able to change the spread to accommodate new market conditions.
Variable Spread
A variable spread is set by the broker within the lower limit and may fluctuate or be influenced by changes in the currency value.
With a variable/floating spread, its value depends on the current market situation, including the volatility level. The size of a spread increases due to significant price movements. Most currency pairs have a floating spread.
Advantages
- Traders don't have to worry about requotes because the variation in the spread takes into account changes in the market.
- It provides better pricing by dealing with prices from different liquidity providers. This leads to more profitable pricing due to competition.
Disadvantages
- Trading risks increase significantly since a spread may look profitable but reverse in the blink of an eye.
- A variable spread widens in accordance with increased liquidity and is actually only low during market inactivity.
- It may even trigger protective stops and limits unintentionally.
Spread Trading Strategies
Spread trading strategies in the classical sense (that is, the difference between the Bid and Ask prices of the same asset) don't exist. Some novice traders take an integral hedging strategy on a spread, but this is a slightly different example of trading, and we use the word "spread" differently.
Spread trade with integrated hedging

Integral hedging on a spread is, first of all, a hedging strategy. The word "spread" here means a different definition and is more slang.
As part of this strategy, the trader chooses two interrelated assets and opens trades in opposite directions.
It can be, for example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD. On the first currency pair, you open a trade to buy. On the other one, a trade to sell. In this situation, you don't need to put a stop-loss since setting one can lead to additional losses. Protection against excessive risks arises from hedging.
The logic of the strategy is simple: if the trader is unsure in which direction the asset will move, he ensures it with a reverse transaction on the correlating instrument.
If the main asset moves in the right direction, then at some point, the trader buries the trade first for an additional one and then for the main asset (when net profit appears on it).
The strategy of integral hedging on the spread was originally designed to trade shares of the stock market. There were fundamental prerequisites for this strategy: transactions were always opened to buy stocks of an industry leader (for example, McDonald's) and sell shares of its main competitor (for example, KFC).
Next, there are two scenarios:
- In a calm market, McDonald's shares will show about twice as much growth as KFC shares. This will be the trader's profit.
- In the event of a market correction or downturn, the price of the shares of both companies will decrease, and the trader will close both trades to about zero.
Thanks to the CFD tool, the same transaction can be easily implemented in the forex market.
Advantages
- Flexible system of protection against risks due to hedging.
- Stable profits in a calm market.
- Minimal losses (or lack thereof) in case of a market downturn.
Disadvantages
- Relatively low level of profit (10-20% per annum).
- The strategy is ineffective in the short term.
Conclusion
These are the basics of using spreads in trading, which will improve your trading skills. Having this expertise in your arsenal, apply it to your advantage to trade in Libertex. Trading requires a proper platform.
- Convenient interface and versatility. The Libertex platform was designed to keep an already familiar basis but make access easier and more user-friendly. All assets are sorted by maximum growth and decline indicators, which makes it possible to quickly find the right currency pairs.
- Improved graphical analysis. The tools for graphical analysis and a set of technical indicators surpass those available in the original MT4. Following the original example, there are three types of standard graphs in the working area.
- Technical analysis.The set of standard indicators is significantly expanded with a total number of 43.
Improving your skills is a step-by-step process, which takes some time and practice. Register a free Demo account to practice your strategy of choice!
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to be and does not constitute investment advice or any other form of advice or recommendation of any sort offered or endorsed by Libertex. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Why trade with Libertex?
- Get access to a free demo account free of charge.
- Enjoy technical support from an operator 5 days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. (Central European Standard Time).
- Use a multiplier of up to 1:30 (for retail clients).
- Operate on a platform for any device: Libertex and MetaTrader.