

What is a Stop-Loss Order and How to Use it in Trading
However, some beginners who have started the trading do not fully understand what stop-loss is and why it should be exposed. In this article, we will examine all of the main points related to a stop-loss order and consider several effective strategies for placing stop orders.
Stop-Loss Definition
A stop-loss is an auxiliary order set to protect a trader from serious losses in a particular transaction.
If the price goes in the wrong direction from which a trader expected movement, and the trade becomes unprofitable, the stop-loss helps save the stock.
When the price reaches the stop-loss level, the transaction closes automatically. The trader is able to save the rest of their money and can begin developing a plan to return their losses. The trader himself assigns a stop-loss level before opening a trade. A stop-loss is always tied to a certain price (with the exception of a stop-loss on time, which will be discussed later).
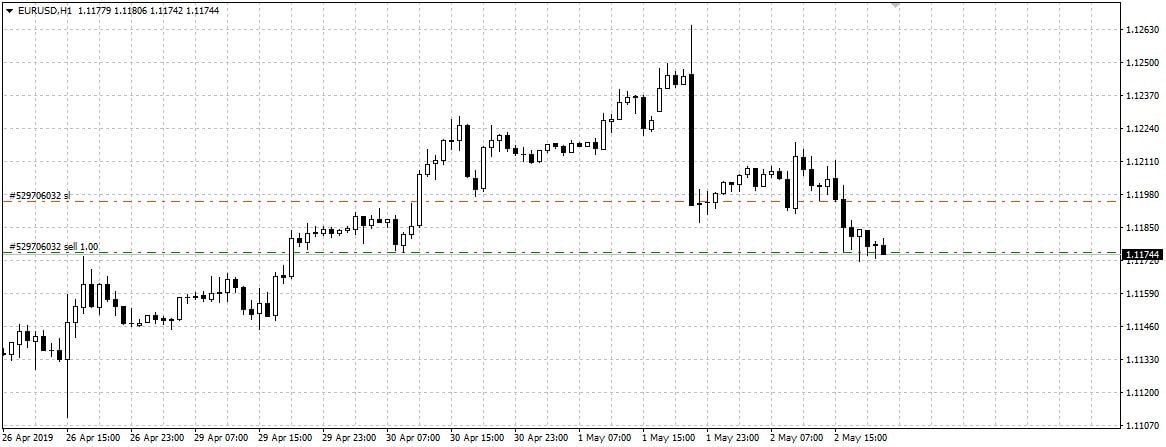
For example, if a trader opens a EUR/USD trade to buy at a price of 1.2500, then the stop-loss can be set at 1.2490. It means that if the price goes down and a trader starts to suffer losses, the loss will be a maximum of 10 points. After that, the transaction will be closed, and a trader can make a new decision. For example, open a transaction for sale if the trend of price reduction continues.
Why Use a Stop-Loss in Trading and How to Place It Correctly
A stop-loss must be set in order to minimise and control possible losses during trading. Even the best trading strategy periodically gives false signals, and opening trades with these signals leads to losses. A stop-loss helps to reduce these losses to a minimum, which allows a trader to quickly compensate for the lost funds and again get a plus.
A stop-loss can be set both at the time of opening the transaction and later. It is better to place a stop order immediately because sometimes the price can make a sharp jump and move 20-30 points in just a few seconds.
If such a jump occurs in the opposite direction than the trader expected, a stop-loss will reduce losses many times. If a sharp price fluctuation occurs immediately after the opening of the transaction, in which the stop-loss was not set in advance (for example, a trader decided to do it a little later), the funds will be, to some extent, defenceless.
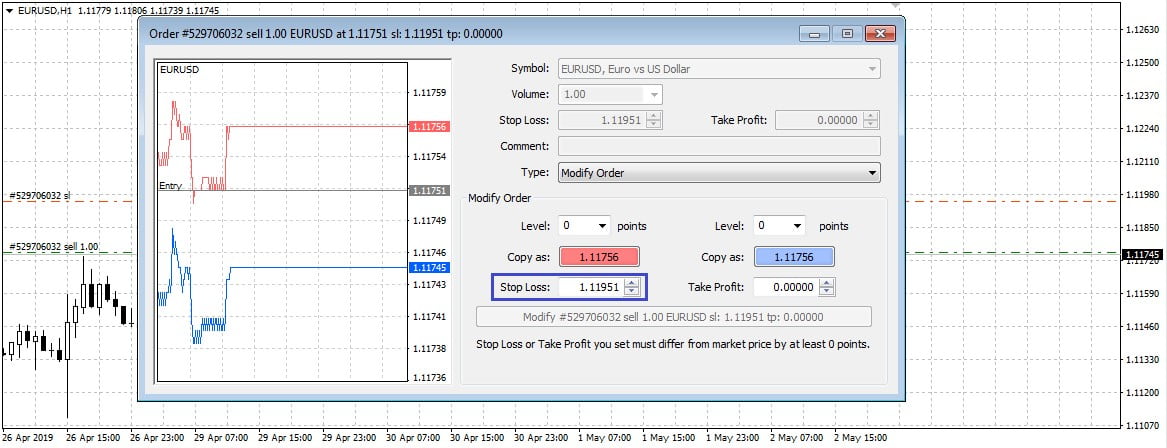
In practice, it is very easy to set stop-loss. For example, in the popular MetaTrader 4 trading platform, this can be done in at least two ways:
- When opening a new order, enter the stop-loss level in the price level at which you would like to place a stop-loss and close the trade.
- When the trade is already open, you need to hold down the left mouse button by hovering the cursor over the order line and dragging the line in the opposite direction to the open trade. For example, if you have opened a purchase transaction, you need to drag the line downwards or upwards for a sale.
How to Calculate Stop-loss
There are many ways to calculate the size of the stop-loss for each specific transaction. In most professional trading strategies, it is already written, under what conditions, and at what distance from the opening price of a transaction, a stop should be placed. There are also several universal tactics for calculating and installing a foot. We'll discuss them later in this article.
There is also one well-known rule that is recommended for all traders and for beginners in particular. The rule is this: losses in each individual transaction should not exceed 2% of the total capital. Based on this, you can calculate the stop-loss.
For example, a trader has a capital of $10,000 and opens a EUR/USD transaction with a volume of 1 lot. The calculation is as follows:
- 1 lot EUR/USD = €100,000, one point of price movement will cost $10.
- 2% of the capital of a trader is $200.
- 200/10 = 20. So, a trader can afford a drawdown of a maximum of 19 points before forcibly closing trades and fixing a minus. The stop order must be placed at a distance of 20 points from the opening price of the transaction.
Types of Stop-losses

There are at least three types of stop-losses, each of which works differently and allows a trader to rely on a different result.
Basic Stops
The standard stop-loss that most brokers offer on their platforms works as follows:
- A trader places a stop order at a specific price.
- When the real market price reaches this mark, the transaction closes.
- Stop-loss is set once and remains unchanged (if a trader does not change it himself, manually).
The main drawback of such a stop-loss is that it is subject to "slippage”. If the price makes a sharp jump of several points and the stop-loss "jumps", the transaction will close, not on the level indicated by a trader, but only on that level where the price jumped to. It means that a trader can lose a few points more than he allowed for according to this plan.
Guaranteed Stop-loss
Guaranteed stop works on the same principle as the base, but it has one significant difference. When a guaranteed stop-loss is triggered, the transaction will always be closed precisely at a price set by a trader.
In other words, the guaranteed stop is not subject to slippage. The broker undertakes to close the transaction at a certain price and assumes all the risks associated with volatility. However, for such a guarantee, the broker may assign an additional commission.
Trailing Stop
A trailing stop is different from the base and guaranteed that it can move after the price stops.
The trailing stop is not set at any particular price point. It is tied directly to the current price - for example, it might be set at a distance of 20 points.
If the price moves in the necessary direction a trader plans for, the trailing stop “pulls” behind it, always remaining at a distance of 20 points. If the price turns in the opposite direction, the stop-loss remains in place.
Using a trailing stop, a trader can not only ensure against excessive losses but also protect part of the profits. A trailing stop can be used as a method of taking profits, instead of the standard Take Profit.
Stop-loss Strategies
If your trading system does not provide any specific conditions for placing a stop order, you can use one of the universal strategies.
Percent Stop-loss
The percentage stop is set in a certain relation to constant values, such as the amount of capital or the level of a Take Profit.
This involves placing a stop order, based on the size of the capital, we have already considered earlier. The recommended ratio of stop loss to capital is 2:100 (i.e., 2%). For example, with a capital of $10,000, For example, if your capital is $10,000, it will be correct to put a stop loss at about $200. Binding to take profit is usually 1:2 or 1:3 - that is, the planned profit must be 2 or 3 times higher than the allowable loss.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
The advantages of such tactics are obvious - the stop level is easy to calculate, and its goal is to ensure the profit in one transaction is many times greater than the loss (although, this goal is not always met). However, it is far from reasonable to set a stop-loss with such tight binding in every situation and to ignore the objective situation in the market.
If the stop-loss set in a ratio of 1: 3 to take profit is in front of a key level, the probability that the price will affect such an order is very high. In this case, the frequency of closing trades using stop-losses can negate the profit obtained due to the relatively large take profit.
Volatility Stops
Setting a stop-loss based on volatility is an effective technique since in this case a trader can take the stop beyond the main range of price fluctuations and ensure that the order that will be accidentally “touched”.
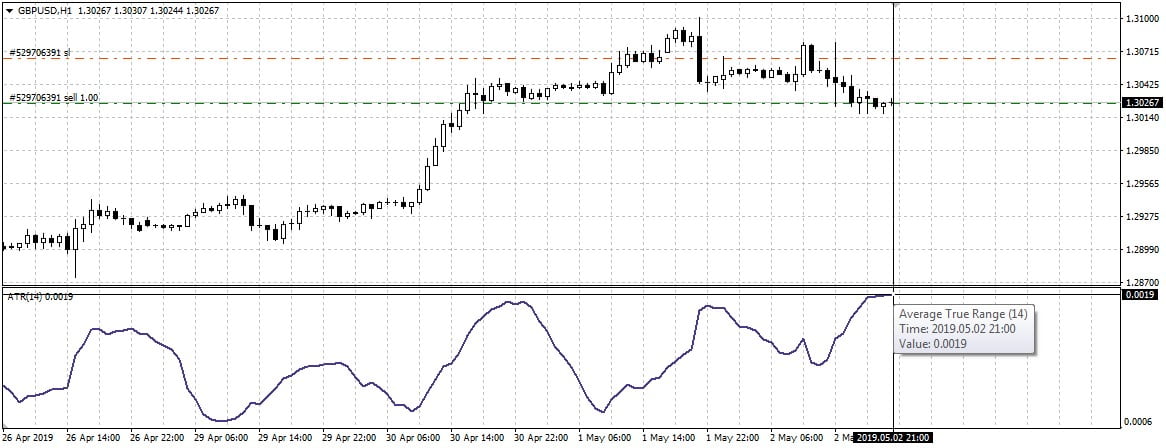
To determine volatility, simple indicators like Standard Deviation (SD) or Average True Range (ATR) are most often used. The calculation of the stop-loss is as follows:
- A simple moving average (SMA) is set on the chart to determine the average price indicator.
- Next, an ATR or SD indicator is installed to determine volatility.
- To determine the price for a stop order, the last ATR (SD) value multiplied by 2 must be subtracted from the last SMA value.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Stop-loss on volatility may be the best option at the time of exposure, but its relevance decreases with each new candle on the chart. For medium and long-term trade, this method is not recommended.
Chart stop
When installing a stop-loss on the schedule, key levels (support and resistance), as well as local extremes are taken into account. They need to be determined before setting a trade open and setting a stop. This tactic to set a stop-loss is most effective when trading according to technical analysis. In this provision, the definition of levels, extremes, and other important elements occur in the general analysis of the graph.
Stop-loss should be set beyond the nearest level or local extreme. If the stop is set at the level itself or in front of it (relative to the price), the likelihood that it will be affected by random fluctuation increases.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Stop-loss by time
Stop-loss of this type is set based not on price indications but on time parameters. For example, a trading strategy may require a trader to close a trade at the end of the day, regardless of the outcome.
This stop-loss is not very popular and is used in rare cases.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Conclusion
A stop-loss is an important element of the trading system. It makes trading more secure and controlled. It can be difficult for a novice trader to understand all the nuances of placing a stop-loss immediately, so the best option would be to start with mastering the simplest techniques.
For trading training and working with stop-loss, the Libertex trading platform is perfect.
Unlike other trading platforms, it is very intuitive, and even a novice who has no trading experience will quickly learn how to navigate its functionality. In addition, you can open a demo account for free at Libertex and practice on it as long as it takes for you to improve you skills the platform.
For all its convenience and intuitiveness, Libertex offer a wide range of features and a large selection of assets and tools for analysis. On this platform, a novice trader will be able to try out all the strategies for placing stop-loss and, after evaluating the results, make an optimal selection.
FAQ
Percent Stop-loss
The percentage stop is set in a certain relation to constant values, such as the amount of capital or the level of a Take Profit. This involves placing a stop order, based on the size of the capital, we have already considered earlier. The recommended ratio of stop loss to capital is 2:100 (i.e., 2%). For example, with a capital of $10,000, For example, if your capital is $10,000, it will be correct to put a stop loss at about $200. Binding to take profit is usually 1:2 or 1:3 - that is, the planned profit must be 2 or 3 times higher than the allowable loss.
Volatility Stops
Setting a stop-loss based on volatility is an effective technique since in this case a trader can take the stop beyond the main range of price fluctuations and ensure that the order that will be accidentally “touched”.
Chart stop
When installing a stop-loss on the schedule, key levels (support and resistance), as well as local extremes are taken into account. They need to be determined before setting a trade open and setting a stop. This tactic to set a stop-loss is most effective when trading according to technical analysis. In this provision, the definition of levels, extremes, and other important elements occur in the general analysis of the graph. Stop-loss should be set beyond the nearest level or local extreme. If the stop is set at the level itself or in front of it (relative to the price), the likelihood that it will be affected by random fluctuation increases.
Stop-loss by time
Stop-loss of this type is set based not on price indications but on time parameters. For example, a trading strategy may require a trader to close a trade at the end of the day, regardless of the outcome.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to be and does not constitute investment advice or any other form of advice or recommendation of any sort offered or endorsed by Libertex. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Why trade with Libertex?
- Get access to a free demo account free of charge.
- Enjoy technical support from an operator 5 days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. (Central European Standard Time).
- Use a multiplier of up to 1:30 (for retail clients).
- Operate on a platform for any device: Libertex and MetaTrader.