

What Are Cryptocurrencies, and How Do They Work?
In the near future, you'll have trouble finding a major bank, a large accounting firm, a prominent software company or a government that hasn't used cryptocurrencies or started a project using blockchain.
What are cryptocurrencies?
The term 'cryptocurrency' has many definitions. It's a digital currency created from a computer code, i.e., a string of coded data to indicate a currency unit. Cryptocurrencies are also known as digital currencies. The most popular crypto is Bitcoin. Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies are free of government regulation and manipulation and are monitored through peer-to-peer Internet protocols.
Crypto coins are created through mining, that is, by adding transaction records to the public ledger. Cryptocurrency transactions occur instantly and must be confirmed to be finalised. They aren't reversible or falsifiable once confirmed.
To have an in-depth understanding of cryptocurrencies, you need to wrap your head around their revolutionary, transactional and monetary properties.
Revolutionary features of cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies differ from fiat currencies by their revolutionary features:
- They don't have a regulatory body, i.e., a government or a central bank, that can create or influence its supply or demand.
- They aren't just entries in a database, as is the case with conventional currencies.
- Cryptocurrency databases can't be changed by anyone.
Cryptocurrencies derive their name from the fact that their consensus maintenance is ensured by using strong cryptography. Unlike regular currencies, cryptocurrencies are guaranteed by mathematics, not by trust or people.
This makes crypto a favourable alternative to fiat currencies.
Transactional features of cryptocurrencies
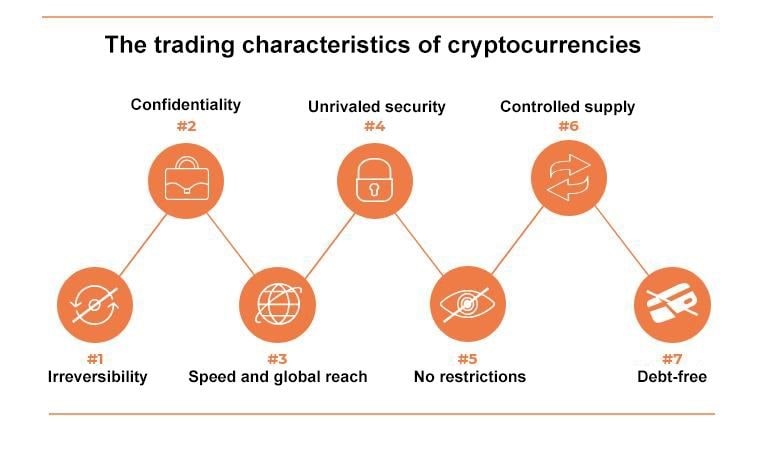
Irreversibility
Cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible. Once confirmed, no one can reverse them, not even government agencies, the cryptocurrencies' respective creators or miners.
Confidentiality
Cryptocurrencies also offer various levels of anonymity, which means that accounts and transactions involving cryptocurrencies are difficult, if not impossible, to connect to a real-world identity. Bitcoins are received through addresses that are simply random strings of approximately 30 characters. Although it's possible to track the flow of cryptocurrency transactions, it's very difficult to connect addresses with the identities of real-world users.
Speed
Cryptocurrency transactions can be confirmed in a matter of minutes.
Global reach
Cryptocurrency transactions take place in a worldwide network of computers that aren't affected by a user's physical location. You can send/receive money from anywhere.
Unmatched security
Cryptocurrency funds are locked securely in a cryptographic system that only the owner can access with a private key. Cryptocurrencies are protected by strong cryptography and numbers that are impossible or near impossible to break, depending on the particular cryptocurrency.
No restrictions
You're free to use your cryptocurrencies as you wish. You don't need any permission to use bitcoins. You can download the corresponding cryptocurrency software for free, install it and start receiving and sending coins.
Monetary features of cryptocurrencies
Controlled supply
Cryptocurrencies are attractive compared to fiat currencies because their supply is controlled. The supply of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin decreases with time and is controlled using schedules written in the code. This simply means that the supply of any cryptocurrency at any time in the future can be estimated today.
No debt
Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies aren't created by debt. The cryptocurrencies represent themselves.
How do cryptocurrencies work?
Transactions are sent between pairs from cryptocurrency wallets by matching public codes related to users' private passwords (also known as cryptographic keys). Transactions carried out between peers are recorded in a public ledger of transactions known as a blockchain. All users of the same cryptocurrency have access to the general ledger if they choose to download a full-node wallet (instead of keeping their currencies in a wallet or a virtual wallet such as Coinbase). The amounts of the transactions are public, but the number of the account that sent the transaction is encrypted.
Each transaction arrives in a digital cryptocurrency wallet. The entity that possesses the wallet password has the amount of cryptocurrency indicated in the general ledger.
When someone sends or receives cryptocurrencies from one wallet to another using a set of private and public passwords, that transaction is queued to be added to the general ledger. Many transactions are added to one ledger at a time in a sequence. That's why the ledger and the technology behind it are called a blockchain. It is a "chain" of "blocks" of transactions.
History of cryptocurrencies
The history of cryptocurrencies is short-lived thus far. Yes, there were some digital currency systems before. Previous versions of digital currencies were strictly centralised, while new ones are decentralised.
Now, what is really interesting about cryptocurrencies is that they never intended to be invented as they are known today. Actually, it all started with the now-famous Bitcoin and an unknown individual named Satoshi Nakamoto.
Nakamoto's initial goal was to create only an electronic peer-to-peer box system. For a long time before that, people had tried to create some kind of online digital cash system but always failed due to centralisation problems.
Nakamoto knew that another attempt to build a centralised cash system online would only result in more flaws, so he created a digital cash system without a centralised authority. And that's how Bitcoin was born. Bitcoin is intended to be owned by the entire Bitcoin community.
When Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2008, its value skyrocketed. At first, it was worth a little more than a penny. Now, however, its price is exponentially higher than its initial value.
Returning to the creation of Bitcoin, the serious issue faced by Nakamoto was to stop double-spending. The expenditure and amount of digital money present in the digital world were controlled by a central authority, so the previous digital currencies were always subject to centralisation. In a decentralised digital currency system, each user or entity must agree on the balance and transaction of each account so that the entire system works.
However, Nakamoto was able to create this system of cryptocurrencies, in which a complete consensus of all parties is required. If there's a disagreement between them, everything breaks down. All this could seem very complicated and almost impossible to execute, but Nakamoto and his invention of Bitcoin proved that notion wrong. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies demonstrate no need of any kind for a central authority to control spending and account balances, provided there's full consensus among all parties involved.
Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin have demonstrated their value and ability to operate in the real world. Increasingly more banks, investment firms, commercial organisations and even retailers have begun to accept them as legitimate forms of payment.
The most common cryptocurrencies
Since Nakamoto revealed his amazing innovation, dozens of decentralised cryptocurrencies have been launched. There are now over 1,700 cryptocurrencies, and this number continues to grow. Some of the most popular and most valuable cryptocurrencies at the moment are:
- Bitcoin. The cryptocurrency with which it all began. It's the most popular digital currency in the market, although its legal status may vary depending on the country.
- Ethereum. A programmable coin that uses the bases that Turing founded. It allows developers to create different distributed applications and technologies that don't work with Bitcoin.
- Bitcoin Cash. A Bitcoin fork, its origins are recent, but its value has soared, boosting its market capitalisation.
- Bitcoin Gold. A project based on Bitcoin that uses other types of algorithms for encryption. For everything else, it follows the guidelines of the basic Bitcoin project.
- Litecoin. A cryptocurrency that was created to be the 'digital silver' compared to the 'digital gold' of Bitcoin. It's also a Bitcoin fork, but unlike its predecessor, it can generate blocks four times faster and has a supply cap that's four times higher (84 million).
- Ripple. Unlike most cryptocurrencies, it doesn't use blockchain to reach a consensus across the network for transactions. Instead, an iterative process of consensus is implemented, making it faster than Bitcoin and making it vulnerable to hacker attacks.
- Dash. A two-tier network whose first tier is the miners who secure the network and record transactions and whose second one consists of master nodes that retransmit transactions and enable transaction types InstantSend and PrivateSend. The first is significantly faster than Bitcoin, while the second is completely anonymous.
- BXP Chip Coin. The first Mexican cryptocurrency, it can be used and invested or bet on its development.
What can you do with cryptocurrencies?
You can buy things
You can use cryptocurrencies for online and offline payments, such as for hotels, flights, jewellery, apps, computer parts and more.
You can invest
Cryptocurrencies are considered some of the most attractive investment options available right now. Many people see great potential in cryptos and invest without any hesitation. Some people claim to have become millionaires through their investments in cryptocurrencies.
Commercial payments
You can accept cryptocurrencies as payment just like you would with cash. You can also withdraw cash; Coin ATM Radar currently lists over 37,000 ATMs in 77 countries as of May 2022.
The cryptocurrency market in Mexico is among the largest in Latin America. Exchange, digital and even real estate companies work with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. All types of businesses already accept these payment methods, and the acquisition of these assets is possible even in convenience stores such as Seven-Eleven.
How to obtain cryptocurrencies
You can obtain crypto through the following methods:
- Buy them with fiat money (current)
- Receive them for goods or services provided
- Generate them through mining
- Lend or exchange them
Buying

As with any investment, you must buy and sell crypto through an exchange platform, which requires you to create an account and store the cryptocurrency in your own wallet. You must also place the total value of the asset to open a position.
To trade cryptocurrencies, you'll need access to an exchange platform. If you aren't familiar with how they work, you'll need to overcome the learning curve by studying the technology involved and how to make sense of the data.
You'll also need an account to trade on an exchange platform. These can be:
- Slow to acquire. Getting an account usually takes a few days since the approval is done manually.
- Restrictive use. As a new account owner, you're probably limited to a deposit of a few hundred dollars per week.
- Expensive to maintain. Funds and withdrawals generate commissions, while some large exchanges only accept bank transfers, which may take several days.
Furthermore, these young companies can be slow to solve even direct customer service problems without infrastructure accumulated over years of commercial activity.

Trading CFDs (contracts for difference) involves speculating on whether the chosen market will increase or decrease in value. Prices are quoted in traditional currencies, and you never take possession of the underlying cryptocurrency itself.
CFD trades are leveraged products that allow you to open a position with a fraction of the total value of the trade. In other words, you can get large exposure to a financial market while only mobilising a relatively small amount of capital. Just remember that while this can increase your profits, it can also result in substantial losses.
In addition, because it's unnecessary to deal with an exchange, you could be ready to operate in much less time.
Our online trading platform has an extensive resource library. Please keep in mind that crypto CFDs are not available for retail clients.For more educational information on financial topics, check out the other posts on our blog! At Libertex, we regularly publish articles for investors learn about their options, from cryptocurrency predictions to CFD explanations. When trading CFDs cryptocurrencies, you won't directly access the underlying exchange. We interact with the market on your behalf.

Cryptocurrency mining is the processing of transactions in the system of digital currencies. In the case of Bitcoin, its current transaction records, known as blocks, are added to the past transaction record, known as the blockchain.
How does blockchain work? When a point-to-point cryptocurrency transaction is performed, it's sent to all users with "full node" wallets. The specific types of users called miners then try to solve a cryptographic enigma using software, which allows them to add a "block" of transactions to the general ledger. Whoever solves the puzzle first will receive a few coins as a reward.
Sometimes, the miners gather the power of computing and share the earned coins. This practice is known as a "mining pool". The algorithm is based on consensus, which means that if the majority of users trying to solve the puzzle send the same transaction data, the transaction is confirmed as correct.
A digital currency is defined by the digitally signed record of its transactions, beginning with its creation. The block is an encrypted hash job test created in an intensive calculation process. Miners use software that accesses their processing capacity to solve algorithms related to transactions. In return, they receive a certain number of digital coins per block. The blockchain avoids attempts to duplicate digital currencies; otherwise, the digital currency could be falsified by copying and pasting.
Originally, the digital extraction of coins was done in the CPUs of the individual computers, with more cores and a higher speed, which resulted in greater profitability. After that, the system came to be dominated by multi-graphics card systems, then programmable gate arrays (FPGA) and finally specific application integrated circuits (ASICs), in an attempt to find more results with less use of electrical power.
Due to this constant climbing, starting has become difficult for potential miners. This adjustable difficulty is an intentional mechanism created to avoid inflation. To avoid this problem, people often work in groups to form mining pools.
Bitcoin started with individuals and small mining organisations. At that time, the start-up could be enabled by a single high-end gaming system. Now, however, the largest mining organisations can spend tens of thousands on specialised high-performance computers. In the world of malware, one of the most prevalent current threats is stealth mining by bots, in which user systems mine digital currency on someone else's hardware without the owner's knowledge. The funds are channelled to whoever controls those bots.
The Bottomline: pros and cons

We have gathered all the pros and cons of the ways to obtain cryptocurrencies. Please bear in mind that all types of cryptocurrency operations carry risk.
|
Way to obtain cryptocurrencies |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Buying |
|
|
|
Trading CFDs |
|
|
|
Mining |
|
|
*All types of currency transactions involve risks. Loss may exceed the initial deposit.
Final considerations
The future that 20th-century science fiction writers spoke of has arrived! Digital currencies not owned by any state or controlled by any one individual are used to the maximum for non-monetary settlements and can serve as a means to generate wealth for thousands of enterprising and forward-thinking Internet users.
The cryptocurrency market is still relatively young, and the most optimistic investors believe there's a bright future ahead. However, the above information shouldn't be taken as investment advice. It's only for general knowledge purposes. You must do your own research before trading any CFDs cryptocurrency.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to be and does not constitute investment advice or any other form of advice or recommendation of any sort offered or endorsed by Libertex. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Why trade with Libertex?
- Get access to a free demo account free of charge.
- Enjoy technical support from an operator 5 days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. (Central European Standard Time).
- Use a multiplier of up to 1:30 (for retail clients).
- Operate on a platform for any device: Libertex and MetaTrader.