

What is the DAX 30 Index?
The DAX explained
The DAX is the headline index that includes the 30 most valuable companies listed on German stock exchanges.
It represents approximately 75% of the total value of publicly listed German companies. Its value is published by the Deutsche Börse Group and calculated using prices from the Xetra electronic exchange, a subsidiary of Deutsche Börse.
DAX Definition
DAX stands for Deutscher Aktienindex, which means the German stock index. TheDAX 30 is sometimes referred to as the GER30 or the DE30.

DAX 30 History
The DAX 30 index was initially launched in 1988 with a base value of 1,163. Approximately half of the original index constituents are still included in it.
The index used prices from the Frankfurt Stock Exchange. However, since 1999, prices have been sourced from the Xetra electronic trading system.
Over time, many of Germany's largest firms have become multinational companies. The DAX 30, therefore, represents far more than just the German economy.
Numerous derivatives and index-tracking products based on the DAX 30 have been launched as the years passed. These can be traded on exchanges worldwide.
Understanding the DAX 30
The DAX is a market capitalisation-weighted index that includes the 30 largest German companies. To qualify for index membership, companies must be included in the Prime Standard market in Germany. The list of stocks is reviewed quarterly.
How is the DAX 30 index calculated?
The index is weighted by market capitalisation. However, each company's weight is capped at 10%. In addition, restricted shares are excluded when the market value of each company is calculated.
Each company's weight in the index represents the company's market value as a percentage of the total market value of all 30 companies.
Companies are removed from the index if their market value falls outside of the largest 45 companies. Companies are considered for inclusion when their value falls within the largest 25 companies.

DAX 30 Weighting and DAX Composition
The following table includes the members of the DAX 30 index as of 20 April 2020. It also features the stock price, market capitalisation and index weight of each company.
|
Company |
Ticker |
Price (€) |
Market Cap $Mn |
Market Cap €Mn |
Weight |
|
SAP SE |
SAP |
109.57 |
139,095 |
127,967 |
10.0% |
|
Linde PLC |
LIN |
184.58 |
97,038 |
89,275 |
9.7% |
|
Allianz SE |
ALV |
166.63 |
71,696 |
65,960 |
8.7% |
|
Siemens AG |
SIE |
83.78 |
70,421 |
64,787 |
8.5% |
|
Bayer AG |
BAYN |
63.14 |
67,063 |
61,698 |
6.8% |
|
BASF SE |
BAS |
47.06 |
45,202 |
41,586 |
5.9% |
|
Adidas AG |
ADS |
207.8 |
43,699 |
40,203 |
5.0% |
|
Deutsche Telekom AG |
DTE |
12.978 |
66,604 |
61,276 |
4.5% |
|
Daimler AG |
DAI |
30.073 |
33,988 |
31,269 |
3.9% |
|
Muenchener AG |
MUV2 |
210.95 |
31,226 |
28,728 |
3.5% |
|
Deutsche Post AG |
DPW |
27.47 |
35,753 |
32,893 |
3.2% |
|
Volkswagen AG |
VOW3 |
127.51 |
69,958 |
64,361 |
3.1% |
|
Deutsche Bourse AG |
DB1 |
141.05 |
27,994 |
25,754 |
2.5% |
|
Infineon Technologies AG |
IFX |
16.391 |
21,353 |
19,645 |
2.4% |
|
Vonovia SE |
VNA |
45.22 |
26,141 |
24,050 |
2.3% |
|
BMW AG |
BMW |
52.56 |
35,971 |
33,093 |
2.2% |
|
E.ON SE |
EOAN |
8.872 |
24,794 |
22,810 |
2.0% |
|
Fresenius SE & Co |
FRE |
39.755 |
23,561 |
21,676 |
2.0% |
|
Henkel AG & Co. |
HEN3 |
79.77 |
34,085 |
31,358 |
1.5% |
|
RWE AG |
RWE |
26.165 |
17,372 |
15,982 |
1.5% |
|
Deutsche Bank AG |
DBK |
6.236 |
13,685 |
12,590 |
1.4% |
|
Merck KGaA |
MRK |
108.025 |
49,889 |
45,898 |
1.3% |
|
Fresenius Medical Care SE |
FME |
71.86 |
22,831 |
21,005 |
1.3% |
|
MTU Aero Engines AG |
MTX |
116.175 |
6,345 |
5,837 |
1.3% |
|
Continental AG |
CON |
75.11 |
16,024 |
14,742 |
1.2% |
|
Wirecard AG |
WDI |
105.55 |
17,687 |
16,272 |
1.2% |
|
Beiersdorf AG |
BEI |
94.65 |
23,210 |
21,353 |
1.0% |
|
Heidelbergcement AG |
HEI |
41.905 |
8,785 |
8,082 |
0.9% |
|
Deutsche Lufthansa Group |
LHA |
8.161 |
4,109 |
3,780 |
0.8% |
|
Covestro AG |
1COV |
30.635 |
5,978 |
5,500 |
0.6% |
Source: marketscreener.com
The largest 5 companies account for 44% of the index. The largest 10 stocks account for 66% of the index, and the largest 15 stocks account for under 80%.
The index is well diversified across the following sectors: Financials, Consumer Discretionary, Basic Materials, Industrials, Technology and Healthcare. These sectors each account for between 11% and 17% of the index. The Telecoms, Utilities, Real Estate and Consumer Staples sectors are less prominent; each accounts for between 2% and 5% of the index.
Major industries represented in the index include chemicals, software and automobile manufacturers.
Largest 5 Stocks in the DAX index
The following stocks each account for between 6% and 10% of the index. Accordingly, they're the most important stocks for DAX 30 traders to keep an eye on.
SAP AG is a leading enterprise software company. Large corporations can use SAP's software to run almost every department, including HR, finance, payroll, logistics, warehousing and planning. SAP is now a major cloud software provider and competes with Oracle, Microsoft and Salesforce. SAP is the largest component of the index.

Linde Plc is the world's largest industrial gas company. It operates worldwide through several subsidiaries, supplying gas to various industries. The company is based in Ireland but retains a listing in Germany as it was formed when Linde AG and Praxair merged.
Allianz SE is one of the largest financial services companies in Europe and the biggest one in Germany. It has several subsidiaries involved in insurance and asset management.
Bayer AG is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies. It operates across several segments, including pharmaceuticals, crop science and animal health. Bayer is the manufacturer of Aspirin, Cipro and Roundup.
Siemens AG manufactures a wide range of products related to electrical engineering and communications. It serves the telecoms, manufacturing, auto, energy and medical industries around the world.

Unique features of the DAX 30 index
Unlike most stock indices, the DAX indices are updated daily after the stock exchange closes. This is done by using prices from the futures exchange, which has longer trading hours.
Two different index versions are published: a price index and a total return index. The price index doesn't include dividends, while the more popular total return index assumes dividends are reinvested in the index.
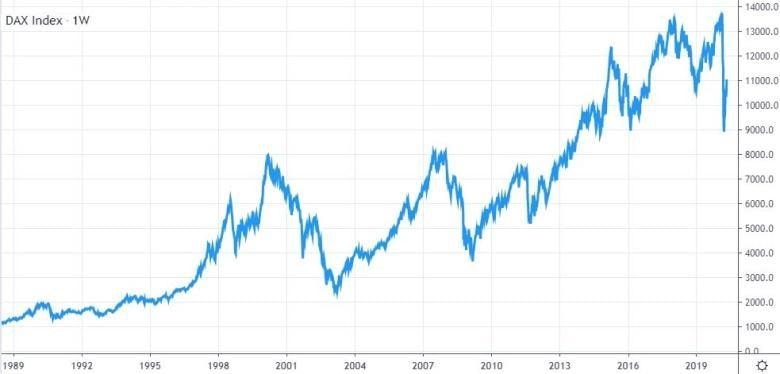
DAX 30's Price Performance
Since its launch, the DAX 30 index has grown in value from 1,000 to approximately 11,000. This represents an increase of 1,000%.
The index's performance is slightly lower than that of the S&P 500, which has returned 1,200% during the same period. Nevertheless, the DAX 30 has been one of the world's top-performing indices over this period.
While the overall performance has been strong, it's also been volatile. The DAX has recorded several declines of more than 30% over the past 30 years. It tends to experience persistent bullish and bearish trends which last anywhere from several months to several years.
The index has been particularly affected by the bursting of the Dotcom Bubble, the Global Financial Crisis and the European Debt Crisis. But it has recovered and continued to make new highs.
Factors influencing the DAX 30 index price
The prominent companies in the DAX 30 index are linked to the strength of both the German and the global economies. Retail brands like Adidas and the major auto manufacturers are affected by consumer spending. Large chemical companies like BASF and Linde are closely correlated to global industrial growth. The hardware and software companies track the global tech sector.
Other DAX Indices
While the DAX 30 is the most well-known stock index in Germany and includes the country's largest companies, there are three other DAX indices to follow.
MDAX
The MDAX index includes midcap companies listed in Germany. These 60 companies rank right after the DAX 30 members but exclude companies in the technology sector. The index was launched in 1996 and included Airbus, Hugo Boss, Osram, Puma and TAG.
TecDAX
The TecDAX index consists of the 30 largest technology stocks listed in Germany that don't qualify for inclusion in the DAX 30.
This index was launched in 2003 and replaced the NEMAX 50.
Notable members include Carl Zeiss, Dialog Semiconductor and Evotec.
SDAX
The SDAX launched in 1999 includes smaller companies that don't qualify for the DAX 30 or MDAX. The index consists of 70 companies.
The largest company is Hapag Lloyd AG, with a market value of $23.9 billion, and the smallest is Metagene AG, with a market value of $109 million.

DAX Index Trading
The DAX 30 index is popular amongst active traders. Its relatively high volatility and strong trends mean it's suitable for trading across all time frames.
Advantages and disadvantages of DAX 30 trading
Advantages
- The DAX 30 price is affected by many industries and economic factors. Meaning the price moves around, often providing frequent trading opportunities.
- The DAX 30 index trading day overlaps both the European and US trading sessions. This allows traders to open positions before the US market opens while still participating in developing trends.
Disadvantages
- Analysing the DAX index can be challenging due to the substantial weighting of all the different companies and sectors.
DAX 30 CFD Trading
An index itself isn't tradeable because it's merely a calculation based on the prices of the constituent stocks. However, you can trade ETFs, futures contracts and contracts for difference (CFDs) on the index.
ETFs are best suited to long-term investors as they're typically not multiplicated. Futures contracts are ideal for active trading but require a large trading account. CFDs are best for active traders with trading accounts of all sizes.
What is CFD Trading?
CFDs are a type of derivative instrument, similar to futures contracts. They allow traders to open both long and short positions using a multiplier. CFDs can be traded on any liquid assets, including indices, stocks, currencies, cryptocurrencies and commodities.
They offer more flexibility than other types of derivatives. You can start trading CFDs with any account size, and you can trade several asset classes using one trading platform like Libertex.
Because CFDs are traded using margin, only a small percentage of the position's value needs to be deposited before making a trade. CFDs are more suitable for short selling than other instruments, although it does not eliminate the inherent risks associated with short trades.
Pros and cons of using CFDs to trade the DAX 30 Index
As with all trading activities and instruments, consider these pros and cons when trading DAX 30 CFDs.
Pros
- You can start trading DAX 30 CFDs with lower requirements for the investment amount.
- CFD trading accommodates smaller trades than futures trading, with a very high minimum trade size.
Cons
- Like any index, the DAX 30 can be unpredictable at times.
- Because the DAX 30 has a long trading day, you may need to keep an eye on the market after the regular trading session.
DAX Trading Strategies
Most traders develop their own trading strategies. The following are some of the more popular approaches for trading the DAX 30 index with CFDs.
The DAX 30 Index is ideal for day trading. Day traders can use momentum, breakout or intraday trend following strategies with CFDs.
Breakout trading
This is a popular approach to day trading the index. A substantial move often follows when a support or resistance level is breached. Breakouts early in the trading day are important as a new trend can develop throughout the European and US trading session.
Swing trading
It's a good strategy if you aren't able to watch the market all the time. The volatility of the DAX 30 index means there are lots of price swings that last anywhere from two days to two weeks. As a swing trader, you can use technical, fundamental analysis or a combination of the two.
Trend following
The DAX 30 index experiences persistent long-term trends that last from a few months to a few years. Less active traders can ride the trend in both directions using CFDs.

Conclusion
The DAX 30 is one of the world's most important stock indices outside the US. It's a good benchmark for the German economy too. It's one of the best indexes to trade for those active during the European trading session. However, it can also be traded during the US session.
You can trade CFDs on the index with Libertex. But please note that trading CFDs with a multiplier can be risky and lead to losing all of your invested capital. Open a risk-free Libertex demo account today to get used to the platform and learn more about trading the DAX 30 index with no risk or cost involved.
Libertexis a broker and trading platform that offers CFDs, stocks, commodities, indices, ETFs and cryptocurrencies with a multiplier of up to 100. The platform provides free trading tutorials and state-of-the-art trading tools.
FAQ
What is the DAX 30 index?
The DAX 30 is the leading index that tracks the performance of the largest German companies.
What moves the DAX 30?
The DAX responds to the local German economy, the performance of the global technology and manufacturing industries.
How to invest in the DAX 30
For long-term investors, DAX 30 ETFs are a good option.
How to trade the DAX 30 index
The DAX is a great index for trading. Most traders use CFDs.
How important is the DAX 30 index to traders?
The DAX is one of the most popular indexes in Europe. It also correlates well with developed global markets and overlaps the European and US trading sessions.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended to be and does not constitute investment advice or any other form of advice or recommendation of any sort offered or endorsed by Libertex. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Why trade with Libertex?
- Get access to a free demo account free of charge.
- Enjoy technical support from an operator 5 days a week, from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. (Central European Standard Time).
- Use a multiplier of up to 1:30 (for retail clients).
- Operate on a platform for any device: Libertex and MetaTrader.